Key points
- The word displace means to push out.
- A more reactive element can displace a less reactive element out of its compound during a chemical reaction.
- Displacement reactions can be used to investigate the reactivity of metals and extract metals from metal oxides.
Video - displacement reactions
Watch this video which explains displacement reactions involving metals.
Displacement reactions in metals
VOICEOVER: Displacement reactions
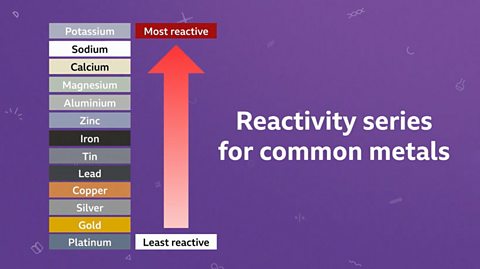
Elements can be placed into a reactivity series with the most reactive element at the top of the list and the least reactive at the bottom. A displacement reaction occurs when a more reactive element displaces, or pushes out, a less reactive element from a compound that contains the less reactive element. After a displacement reaction, the less reactive element is now pure and left uncombined. In industry, we use iron to displace copper from solutions of waste copper compounds, which is really useful. As scrap iron is much less valuable than copper, which we need for many electronic devices such as computers and phones.
Cel: Mrs Roberts, please could you talk us through exactly what we mean by displacement?
Mrs Roberts: Yeah. So, a displacement reaction involves a metal and a compound of a different metal. In a displacement reaction a more reactive metal will displace, which means pushes out, a less reactive metal from its compound.
Cel: So, essentially, sometimes a bigger, stronger metal comes along and pushes the other one out?
Mrs Roberts: Yeah, well a lot of the time students like to think the more reactive element as being stronger and win in a fight with a less reactive element. It's OK to think of it as two metals fighting over a non-metal and winning if that helps you to remember. But you should never use the word stronger.
Cel: Oh. Why is that? And how should we describe it then?
Mrs Roberts: Well, the scientific term is more reactive. Strong means something else in chemistry. It means that a substance doesn't break easily and that's a totally different concept.
Cel: Ah, OK. So, do different compounds react in different ways when we're trying to extract the metal from them?
Mrs Roberts: Yes. So if we were to categorise metals by their reactivity, the most reactive metal would naturally be at the top. So, if I'm going to test you now. So, if a copper is added to a solution of magnesium chloride no reaction occurs. What does that tell you about the reactivity between copper compared to magnesium?
Cel: Well, that the copper is less reactive than magnesium because it couldn't displace the magnesium.
Mrs Roberts: That's right.
In a solution containing copper compounds, what metal can be used to extract copper?
Iron can be dipped into a solution of copper compounds to produce valuable metallic copper.
The displacement reactions of metals
A chemical is described as being reactive if it takes part easily and quickly in chemical reactionWhen chemical bonds are broken and made between atoms, so that new substances (compounds or elements) are made..
Some metals are more reactive than others. Metals can be arranged in order of their reactivity. This is called a reactivity seriesA list of elements in order of reactivity, with the most reactive one at the top. The reactivity series usually includes metals and occasionally some non-metals..
Unreactive metals take part more slowly in chemical reactions or don’t react at all.
displacementA chemical reaction in which a more reactive element displaces (pushes out) a less reactive element from a compound and takes its place. reactions involve a metal and the compoundA pure substance made from two or more elements which are chemically bonded in a fixed ratio. of a different metal. A more reactive metal will displace or push out a less reactive metal from its compound in a displacement reaction. The less reactive metal is left uncombined after the reaction. It is no longer chemically bonded to any other elementA pure substance which is made from only one type of atom. Elements are listed on the periodic table.. It is now a pure element.
Example
Magnesium is more reactiveThe tendency of a substance to undergo a chemical reaction. than copper. When a piece of magnesium is dipped into blue copper sulfate solution, a displacement reaction occurs.
The magnesium displaces the copper, and the products are copper and a solution of magnesium sulfate.
This is the word equation:
magnesium + copper sulfate ‚Üí copper + magnesium sulfate
This is the symbol equation:
Mg(s) + CuSO4(aq) ‚Üí Cu(s) + MgSO4(aq)
This reaction cannot happen in reverse. Copper cannot displace magnesium from a compound because copper is less reactive than magnesium.
Can copper displace magnesium from magnesium chloride solution?
No, copper is less reactive than magnesium. Only a more reactive metal will displace a less reactive metal from its compound.
Working scientifically
Observing displacement reactions
When observing displacement reactions look for a colour change or change in temperature. Record any observations in a results table, using words instead of numbers with units.

When recording a colour change, always include both the starting colour as well as the end colour. For example, from orange to brown.
If it looks like nothing happened, it is better to write down “no visible change” rather than “nothing”. Something might have happened which wasn’t visible.
Find out more about observation and measurement skills.
Using displacement reactions to extract metals from their oxides
Displacement reactions can be used to extract metals from their oxides.
Carbon is a non-metal element which is cheap and easy to find. It is more reactive than some metals, such as copper, iron and lead. This means that some metals can be extracted from their metal oxides using carbon.
The crushed rock is mixed with carbon and heated strongly. An example reaction is:
copper oxide + carbon ‚Üí copper + carbon dioxide
This method will not work for metals like aluminium, which are more reactive than carbon. Carbon cannot displace these metals.
Write an equation to show how carbon can be used to displace lead from lead oxide.
lead oxide + carbon ‚Üí lead + carbon dioxide
Displacement reactions in non-metals
Chlorine, bromine and iodine all react in similar ways. Chlorine is the most reactive and iodine is the least reactive. In these non-metals:
- Chlorine can displace bromine and iodine from their compounds.
- Bromine can displace iodine but not chlorine.
- Iodine cannot displace chlorine or bromine.
- If chlorine is added to a solution of sodium bromide, a reaction occurs:
chlorine + sodium bromide ‚Üí bromine + sodium chloride
- If bromine is added to a solution of sodium iodide, a reaction occurs:
bromine + sodium iodide ‚Üí iodine + sodium bromide
- But if iodine is added to sodium chloride or sodium bromide, no reaction happens. The iodine is not reactive enough to displace those elements.
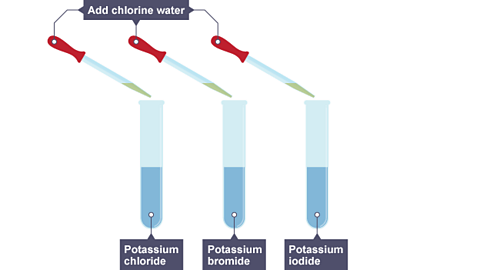
Image caption, Chlorine water is added to three solutions - potassium chloride, potassium bromide and potassium iodide.
Image caption, The results of adding chlorine to these three solutions.
Image caption, Bromine water is added to three solutions - potassium chloride, potassium bromide and potassium iodide.
Image caption, The results of adding bromine to these three solutions.
Image caption, Iodine water is added to three solutions - potassium chloride, potassium bromide and potassium iodide.
Image caption, The results of adding iodine to these three solutions.
1 of 6
If bromine is added to a solution of sodium chloride. What will happen?
No displacement reaction will occur because the bromine is less reactive than the chlorine.
Test your knowledge
Play the Atomic Labs game! gamePlay the Atomic Labs game!
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game.

More on Chemical reactions
Find out more by working through a topic
- count11 of 12

- count12 of 12

- count1 of 12

- count2 of 12
