Geometry and measure
Angles, lines and polygons - OCR
Polygons are multi-sided shapes with different properties. Shapes have symmetrical properties and some can tessellate.

Loci and constructions - OCR
Loci are a set of points with the same property. Loci can be used to accurately construct lines and shapes. Bearings are three figure angles measured clockwise from North.

2-dimensional shapes - OCR
2-dimensional shapes are flat. The perimeter of a 2D shape is the total distance around the outside of the shape. The area of a 2D shape is the space inside the shape.

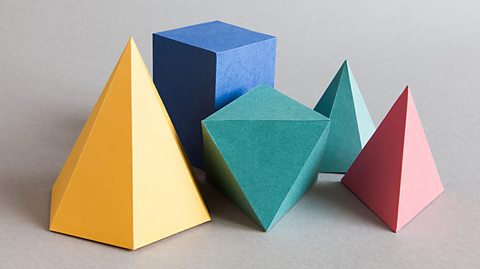
3-dimensional solids - OCR
3-dimensional solids have faces, edges and vertices. Volume is the space contained within a 3D solid. Surface area is the sum of the area of each face. 3D solids can be viewed from different points.
Circles, sectors and arcs - OCR
Circles are 2D shapes with one side and no corners. The circumference is always the same distance from the centre - the radius. Sectors, segments, arcs and chords are different parts of a circle.

Circle theorems - Higher - OCR
Circles have different angle properties described by different circle theorems. Circle theorems are used in geometric proofs and to calculate angles.

Transformations - OCR
Transformations change the size or position of shapes. Congruent shapes are identical, but may be rotated or reflected. Scale factors show how much larger or smaller similar shapes are.

Pythagoras' theorem - OCR
Pythagoras’ theorem can be used to calculate the length of any side in a right-angled triangle. Pythagoras’ theorem can be applied to solve 3-dimensional problems.

Units of measure - OCR
A unit of measurement describes one unit of a quantity. Units of measurement can be imperial or metric. They can be converted using conversion factors.

Trigonometry - OCR
The three trigonometric ratios; sine, cosine and tangent are used to calculate angles and lengths in right-angled triangles. The sine and cosine rules calculate lengths and angles in any triangle.

Vectors - OCR
A vector quantity has both size and direction. Vectors can be added, subtracted and multiplied by a scalar. Geometrical problems can be solved using vectors.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link