Key points
- There are seven types of electromagnetic (EM) waves, which make up the electromagnetic spectrum.
- Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves, and travel at the speed of light.
- Different types of electromagnetic wave have different uses and dangers.
Electromagnetic (EM) waves
There are lots of examples of electromagnetic wavesA group of transverse waves which travel at the speed of light, including radio waves, microwaves and visible light. around us, including light waves, radio waves and infrared radiation. These electromagnetic waves are caused by vibrating electric and magnetic fields and they are transverse waveA wave in which the particles move up and down at right angles to the direction it travels in, like an ocean wave or lifting a rope up and down., because the vibrations of these fields are at right angles to the direction the wave travels.
Electromagnetic waves travel at an extremely high speed: the speed of light. The speed of light in a vacuumEmpty space, where there is no solid, liquid or gas present. is around 300,000,000 metres per second. At that speed, light can travel 7.5 times around Earth in just one second.
A video explaining the range of the electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum
There are seven distinct groups of electromagnetic waves which make up the electromagnetic spectrum.
A mnemonicA pattern of letters, words, ideas or associations which help with memorising something. is often used to help remember the electromagnetic waves in the correct order.
This is a sentence that can remind you of the first letter of each type of wave, in order of increasing frequencyFrequency is the number vibrations of the wave in one second, also seen as the number of complete waves passing a point in one second. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz). – for example:
| Mnemonic | Wave |
|---|---|
| Remember | Radio waves |
| My | Microwaves |
| Instructions | Infrared |
| Visible | Visible light |
| Using | Ultraviolet |
| X-ray | X-ray |
| Glasses | Gamma rays |
Uses of electromagnetic waves
Electromagnetic waves have a wide range of uses. The specific uses depend on the type of electromagnetic wave.

Radio waves
Radio waves are used for sending radio and television signals. They are also used to control radio-controlled toys, like cars, boats and aeroplanes. We even use radio waves in astronomy, to find out about distant stars and galaxies by studying the radio waves they produce.


Microwaves
As well as heating food in microwave ovens, microwaves are used for communication. For example, mobile phones, and wireless internet (Wi-Fi) devices like laptop computers all use microwaves to communicate. Microwaves are also used for sending satellite signals, eg for GPSGlobal Positioning System – a network of satellites used by satellite navigation systems. systems or satellite television.

Infrared
Infrared (IR) waves are emitted by all warm objects, and they are used for heating and to cook food in ovens, grills and toasters. They are also used for communication, including remote controls for televisions and stereos, as well as sending internet and telephone signals along optical fibresA thin piece of glass or plastic, which is used to transmit internet and telephone signals.. Infrared waves can also be detected by infrared cameras, so are often used by night vision cameraA special camera which detect infrared waves, to produce images when there is very little light. or thermal imaging cameraA special camera which can detect infrared waves, to produce images which show the temperatures of objects, or of different parts of an object. in police helicopters – which can detect the infrared waves emitted by people and animals.


Visible light
This is the only type of electromagnetic radiation which is visible to the human eye. As well as allowing people to see the world around them, visible light has a range of other uses, including forming images in cameras and video cameras. Concentrated visible light emitted by laserA device which produces a narrow beam of concentrated visible light. The word laser is an acronym, which stands for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. can be used to send internet and telephone signals along optical fibres. Lasers can even be used in surgery, and to cut materials like wood and metals in a laser cutter.


Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) waves are used in forensic scienceThe use of scientific techniques to help find evidence of a crime. to help detect forged documents, like fake banknotes, passports or driving licences. Ultraviolet waves can be absorbTo take in, and not reflect or transmit waves (eg light). by some materials, like fluorescent inks in highlighter pens, making them glow brightly. They are also used to disinfect water, by killing bacteria.
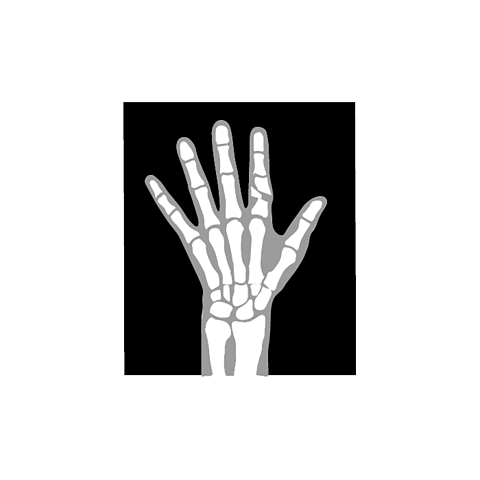


X-rays
X-rays are commonly used to produce medical images of broken bones, because they can pass through body tissues but are absorbed by bones. They are used to sterilise medical equipment, killing any bacteria present before the instruments are used for surgery. X-rays are also used in airport security scanners and to detect broken pipes underground.


Gamma rays
Gamma rays are also used to produce medical images and to sterilise medical instruments, in a similar way to X-rays. They are also used to sterilise food, killing bacteria in fresh fruit and vegetables to increase their shelf life. Gamma rays can also be used to detect and even to treat cancer.

A video about the uses of electromagnetic waves
Can animals detect more of the electromagnetic spectrum than humans?
Some animals can detect infrared, including many species of snake, and this helps them to hunt their prey. Some insects, birds and even reindeer can see ultraviolet rays which leads them to their food source.

Dangers of electromagnetic waves

Although electromagnetic waves have many uses, they can also be dangerous. Different types of EM wave can be dangerous in different ways.
Microwaves
Because microwaves have a heating effect, some powerful microwaves can be dangerous. Your microwave oven will not switch on if the door is open, to prevent the microwaves causing damage to the cells in your body by heating them.
Infrared
The heating effect of infrared waves can cause burns to your skin.
Visible light
Concentrated visible light (eg from a laser or the Sun) can cause eye damage or even blindness.
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation can cause eye damage, which is why most sunglasses can absorb UV, preventing it from reaching the eye. The intense UV emitted by the Sun is absorbed by your skin and can cause sunburn or even damage DNA in your body cells – which could lead to skin cancer.
X-rays
X-rays can also damage DNA in body cells, which could lead to cancers developing inside the body. For low levels of exposure (eg a few medical x-rays per year) this is not a significant problem, but radiographers and other people working with X-rays must take precautions to reduce this risk.
Gamma rays
Like X-rays, gamma rays can also damage DNA in your body cells which can lead to cancers developing inside the body. People working with radioactiveSubstances which emit dangerous nuclear radiation, like uranium or plutonium. which emit gamma rays must limit the amount of gamma radiationSomething which spreads out (radiates) like sound, and light or other EM waves. The term radiation is sometimes used in place of waves – e.g. light radiation or infrared radiation. they are exposed to, by wearing protective clothing and restricting the time they work near these materials.
Wavelengths of electromagnetic waves
Each region of the electromagnetic spectrum has a range of wavelengths associated with it. The range of wavelengths affects the way each type of EM wave behaves and interacts with matter.

Image caption, Radio waves
Radio waves have the longest wavelengths of all EM waves. Radio waves have wavelengths ranging from thousands of metres down to around 30 cm. This means they can easily travel around large objects, like hills, mountains or buildings.
Image caption, Microwaves
Microwaves have wavelengths between around 30 cm and 1 mm. This means they are easily absorbed by fat and water molecules, heating them up.
Image caption, Infrared
Infrared waves have wavelengths which are approximately 1 millimetre or up to one thousand times smaller. Infrared waves are easily absorbed by dark, matt objects and have a heating effect.
Image caption, Visible light
Visible light has wavelengths which are a little less than one thousandth of a millimetre.
Image caption, Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet waves have wavelengths which are a bit shorter than visible light waves. They are small enough to damage DNA in skin cells, which can cause skin cancer.
Image caption, X-rays
X-rays have wavelengths which are approximately one millionth of a millimetre. They pass easily through soft tissues, but are absorbed by bone. X-rays are small enough to enter cells and can damage DNA, which can cause cancers to develop in the body.
Image caption, Gamma rays
You would need a row of around 10 million gamma waves to fill a one millimetre gap. Gamma rays are small enough to enter cells and can damage DNA, which can cause cancers to develop in the body.
1 of 7
Test your knowledge
Play the Atomic Labs game! gamePlay the Atomic Labs game!
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game.

More on Waves
Find out more by working through a topic
- count3 of 15

- count4 of 15

- count5 of 15

- count6 of 15
