Common properties
Electromagnetic waves are members of a family of waves with common properties called the electromagnetic spectrum.
All electromagnetic waves:
are transverse wavesA wave that moves in a direction at right angles to the way in which the particles are vibrating. waves
can travel through a vacuumA volume that contains no matter.
travel at exactly the same speed in a vacuum, the speed of light, 300,000,000 m/s
Like all waves, electromagnetic waves:
transfer energy from one place to another
can be reflected
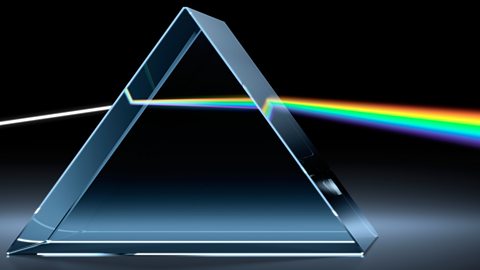
can be refractionProcess by which a wave changes speed and sometimes direction upon entering a denser or less dense medium, eg a light ray changes direction when refracted by a lens.
Differences
Each type of wave in the electromagnetic spectrum has a different:
wavelength
frequencyThe number of waves produced each second. The unit of frequency is hertz (Hz).
The electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is a continuous range of wavelengths.
The types of radiation that occur in different parts of the spectrum have different uses and dangers - depending on their wavelength and frequency.
There are seven members of the electromagnetic family.
Key fact: It is important to remember the order of the electromagnetic spectrum. The following sentence might help:
Rats and Mice In Venice Use eXtra Gondolas.
The order of electromagnetic waves in the spectrum is shown in the table below.
They are arranged in order of decreasing wavelength (and increasing frequency):
| Energy | Frequency | Wavelength | Radiation type | Typical wavelength in m | Typical use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lowest | Lowest | Longest | Radio waves | 1 | Radio and television transmissions, radio frequency identification and astronomy. |
| Microwaves | 1 x 10 -2 | Satellite television and phones, mobile phone calls and microwave ovens. | |||
| Infrared | 1 x 10 -4 | Electric grills, short range communications such as remote controllers for televisions, intruder alarms, thermal images, optic fibres. | |||
| Visible light | 4 x 10-7 to 7 x 10-7 | Vision, photography, illumination. | |||
| Ultraviolet | 1 x 10-8 | Detecting counterfeit bank notes, security marking, sterilising water. | |||
| X-rays | 1 x 10-10 | Medical scanning, security scanners. | |||
| Highest | Highest | Shortest | Gamma radiation | 1 x 10-12 | Sterilising food and medical equipment, detection of cancer and its treatment. |
Communication
Communication between Earth and artificial satellites is mainly by microwaves.
Satellite television and some satellite phones use geostationary satellitesSatellites that always appear at the same point in the sky when viewed from Earth. .
Other satellite phones use low orbit satellitesSatellites that rotate around the Earth every few hours..
All of these waves travel at the same speed in free space, which is the speed of light.
Extended syllabus content: Electromagnetic waves speed
If you are studying the Extended syllabus, you will also need to know the speed of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum. Click 'show more' for this content:
The speed of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum is 3.0 √ó 108 m / s
This is about 300,000,000 m/s (metres per second) in a vacuum and is approximately the same in air.
Extended syllabus content: Systems of communication
If you are studying the Extended syllabus, you will also need to know about the systems of communications that rely on electromagnetic radiation. Click 'show more' for this content:
Many important systems of communication rely on electromagnetic radiation including:
Mobile phones and wi-fi use microwaves because these can penetrate through the walls of buildings and only need a short aerial for their signal to be transmitted and received.
Bluetooth uses radio waves because radio waves pass through walls but the signal is weakened on doing so.
Optical fibres (visible light to infrared) are used for cable television and high-speed broadband because glass they are made of is transparent to visible light and some infrared. Visible light and short wavelength infrared can carry high rates of data.
Video: Waves and communication
In this video, Jon Chase demonstrates how electromagnetic waves are used in communication using an infrared remote control and an outside TV broadcast.
Extended syllabus content: Difference between digital and analogue signal
If you are studying the Extended syllabus, you will also need to know about the difference between a digital and analogue signal and that a sound can be transmitted as a digital or analogue signal. Click 'show more' for this content:
Analogue data is a real-life signal that can vary greatly in value. Examples include:
sound waves
pressure
temperature
Digital data is binary data which represents analogue data. It does not change smoothly from one to another but jumps in a step by step sequence. A digital clock does this. It does not move slowly like the hands of an analogue clock.
Computers and mobile phones work with digital data. Analogue data must be converted to digital before a computer can use it. Sound can be transmitted as an analogue signal when you are speaking, or a digital signal when recorded onto a computer or mobile phone.
Digital signals can be transmitted at a faster rate and further than analogue because the signal can be copied without any excess data (or noise). A mobile phone call from around the world often has the same clarity as one from next door. This is called accurate signal regeneration.
Harmful effects of the electromagnetic spectrum
Over-exposure to certain types of electromagnetic radiation can be harmful.
The higher the frequencyThe number of waves produced each second. The unit of frequency is hertz (Hz). of the radiation, the more energy it carries and the more damage it is likely to cause to the body:
Radio waves: one of the few known effects of radio waves on the human body is a very small rise in temperature of up to 0.2 oC. Some people claim the very low frequency radio waves from overhead power cables and mobile phone base stations near their homes has affected their health, although this has not been reliably proven.
Microwaves can cause internal heating of body cells and tissues.
Infrared radiation is felt as heat and causes skin to burn.
Visible light from a laser which is very intense can damage the retina at the back of the eye.
Ultraviolet can damage skin cells and lead to skin cancer and damage the eyes, it can cause skin to age prematurely.
X-rays damage cells inside the body. They cause dangerous ionisation and when this happens with molecules in living cells, the genetic material of a cell, the DNA is damaged. This can lead to cancer. This is why doctors and dentists stand behind protective screens when taking X-rays.
Gamma rays also damage cells inside the body causing dangerous ionisation in living cells which damages DNA. This can lead to cell death and cancer.
Quiz
Test your knowledge with this quiz on the electromagnetic spectrum.
Teaching resources
Are you a physics teacher looking for more resources? Share these videos on light waves and communication with your students:
More on Waves
Find out more by working through a topic
- count4 of 5

- count5 of 5
- count1 of 5

- count2 of 5