Numeracy skills
Order of operations
Select and carry out calculations in the correct order of precedence using the ‘rules’ of BODMAS (Brackets first then Other then Division then Multiplication then Addition and finally Subtraction).

Multiplication
A number can be multiplied to two decimal places by a single-digit whole number or by multiples of 10, 100 and 1000 using a standard written format and without a calculator.

Division
A number can be divided to two decimal places by a single-digit whole number or by multiples of 10, 100 and 1000 using a standard written format and without a calculator.

Negative numbers
Negative numbers are mainly used with coordinates and temperature. Use negative numbers in addition and subtraction problems including subtracting a negative number.

Distance, speed and time
The distance, speed and time equation allows us to calculate distance, speed and time. In all of these calculations, the units used should correspond with each other.

Rounding
Many calculations result in solutions to a greater degree of accuracy than what is required. In such cases the answers are rounded to the required degree of accuracy.

Rounding and estimating
Select and carry out calculations and round answers to the nearest significant figure. A way of approximating or estimating an answer is to round off using significant figures.
Fractions
Calculations can be carried out using fractions of shapes and quantities. Mixed fractions can be added or subtracted to find the number of fractional parts in a mixed number.
Percentages
Calculations can be carried out using percentages of shapes and quantities. We can calculate percentage increase and decrease, as well as express a quantity as a percentage of another quantity.

Ratio
A ratio is used to compare two quantities which are measured in the same units. Given a ratio, quantities can be calculated.

Financial skills
Budgeting
Working within a budget is important. Budgeting is listing and planning estimated income and expenditure which allows us to make informed choices regarding expenditure and saving.

Income
Income is the amount of money which comes to a person or organisation. All income comes under tax regulations.

Best deal
When deciding upon a purchase it is advisable to find the best deal by comparing information on the product or service being provided, terms on offer and the price of an item.

Converting between currencies
Travelling abroad involves converting currencies into the currency of the country visited. To calculate the amount, exchange rates are used. Some foreign exchange providers charge a commission.

Simple interest
Investigating the impact of interest rates on savings and borrowing. Simple interest is calculated annually using the interest rate. Simple interest is always calculated using the original amount.

Compound interest
In compound interest the amount in interest is added to the original at the end of each year. So the next year the interest is worked out on a larger amount of money.

Saving and borrowing
There are many different ways to save or to borrow money. The interest rate tells you how much extra you could earn from your savings, or have to pay back when you take on debt.

- 2 videos

Statistical skills
Risk and its impact
The link between simple probability and expected frequency is explored using a combination of statistics to investigate risk and its impact on life.
Statistical diagrams
A combination of statistical information can be presented in diagrams. This involves constructing, interpreting and comparing pie charts and cumulative frequency diagrams.
Comparing data sets
Data sets can be compared using averages and measures of spread. A box plot displays information about the range, the median and the quartiles.
Standard deviation
Standard deviation is a measure of the spread of data around the mean value. It is used in comparisons of consistency between different data sets. Two formulae can be used to calculate this.

- 2 videos

Measurement skills
Navigation
A navigation course can be planned using a map or plan. Using bearings and distance, this course can be presented in graphical form. Unknown distances and bearings can be calculated from the diagram.

Container packing
Container packing can be used in many scenarios, such as packing storage boxes for moving, packing shipping containers or filling ferries with vehicles.

Precedence tables
A precedence table is a tool for scheduling activities in planning a project. It is based on the logic of what activities must follow other activities and what activities can run at the same time.

Tolerance
Tolerance is the degree of accuracy required in a measurement or the acceptable range of values in which the measurement will be acceptable. The notation normally used is ± (numerical value).

Geometric skills
Perimeter and area
The perimeter and area of triangles, quadrilaterals (rectangle, parallelogram, rhombus, kite and square), circles, arcs, sectors and composite shapes can all be calculated using relevant formulae.
Volume
Using relevant formulae the volume and surface area of cuboids, cubes, prisms, cylinders, spheres, cones and composite shapes can be calculated.
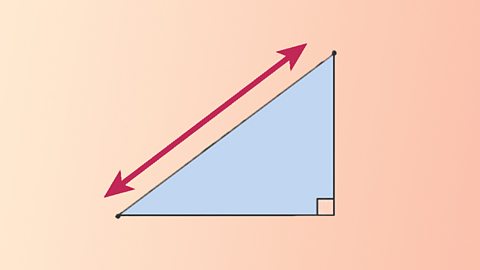
Pythagoras
Pythagoras' Theorem can be used to calculate the length of the third side of a right angled triangle when given the lengths of the other two sides.

Gradient of a slope
Gradient is a measure of how steep a slope or a line is. Gradients can be calculated by dividing the vertical height by the horizontal distance.
- 3 videos
Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link