Exam practice
GCSE Physics: exam-style quiz by topic
Try this quiz based on GCSE Physics past papers. Choose the topic you would like to revise and answer the questions.
GCSE Physics: exam-style questions
Use our interactive tests to understand how the AQA foundation and higher physics GCSE exams work. Revise topics such as forces and learn equations and formulae.
GCSE Physics: quick-fire questions
Free quiz to help you revise for your AQA foundation and higher GCSE exams, based on GCSE physics past papers. Revise formulae, equations and more.

Quizzes
Quiz: Change in energy stores
This interactive quiz is aimed at GCSE physics students studying types of energy store, energy transfers, energy dissipation, the conservation of energy and energy calculations.

Quiz: Energy and heating
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying energy and heating, thermal conductivity, investigating methods of insulation and specific heat capacity.

Quiz: Work, power and efficiency
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying work, power and efficiency, energy and power, efficiency and electrical appliances.

Quiz: Energy demands
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying energy and heating, thermal conductivity, investigating methods of insulation and specific heat capacity.

Quiz: Scalar and vector quantities
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying scalar quantities, vector quantities and calculations involving forces.

Quiz: Moments, levers and gears
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying moments, moments and balanced objects, levers and gears.

Quiz: Forces, acceleration and Newton's Laws
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying terminal velocity, Newton's first, second and third laws and braking.

Quiz: Contact and non-contact forces
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying contact forces and non-contact forces.

Quiz: Gravity
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying gravitational fields, weight, mass, gravitational field strength, calculating work done and free body diagrams.

Quiz: Forces and elasticity
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying change of shape, Hooke's law, energy stored in a spring and how forces affect the extension of a spring.

Quiz: Describing motion
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying motion in a straight line, velocity and acceleration, distance-time graphs, velocity-time graphs and velocity.

Quiz: Pressure in fluids
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying calculating pressure, pressure in a liquid and atmospheric pressure.

Quiz: Momentum - Higher
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying momentum calculations, conservation of momentum and force and momentum.

Quiz: Properties of waves
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying types of waves, wave period and speed, speed of sound in air and measuring waves in a ripple tank.

Quiz: Transverse and longitudinal waves
This interactive is suitable for GCSE physics students studying longitudinal waves, transverse waves, electromagnetic waves, radio waves, microwaves, infrared and visible light.

Quiz: Reflection and refraction
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying reflection of waves and refraction of waves.

Quiz: Lenses
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying convex and concave lenses, real and virtual images, magnification and colour.

Quiz: Sound waves
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying sound waves, ultrasound and seismic waves.

Quiz: Black body radiation
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying emission and absorption of infrared radiation and the Earth's temperature.

Quiz: Electric circuits
This interactive is suitable for GCSE physics students studying electrical circuit symbols, electrical charge and current, potential difference, resistance and voltage graphs.

Quiz: Electric circuits 2
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying series and parallel circuits, resistor networks and energy and power in electric circuits.

Quiz: Mains electricity
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying current, household electricity, alternating current and the National Grid and electrical appliances.

Quiz: Static electricity
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying electrical charges, charging by friction and electric fields.

Quiz: Radioactive decay
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying stable nuclei, nuclear radiation, half life and nuclear equations.

Quiz: Models of the atom
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying developing the atom, Rutherford and the nucleus and further developments to the atomic model.
Quiz: Nuclear fission and fusion
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying nuclear fission, fission reactors and nuclear fusion.

Quiz: Uses and dangers of radiation
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying irradiation, contamination, the effects of radiation on the human body and background radiation.

Quiz: Atoms isotopes and ions
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying structure of the atom, atoms and isotopes and ions.

Quiz: The life cycle of a star
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying the formation and life cycle of stars, main sequence stars and supernovae.
Quiz: The Solar System
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying the structure of the Solar System, the Sun, orbital motion and orbits and speed - Higher.

Quiz: The expanding Universe
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying the red-shift, Big Bang Theory and the future of the Universe.

Quiz: Temperature changes and energy
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying states of matter, internal energy, energy and temperature, specific heat capacity and specific latent heat.
Quiz: Density of materials
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying density, volume and investigating density.

Quiz: Particles in gases
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying particle motion, gas pressure and temperature, gas pressure and volume and changing gas pressure - Higher.

Quiz: Scientific skills
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying planning, observing, analysing, evaluating an experiment and scientific equipment.

Podcasts
Forces
Learn all about forces for your GCSE physics exams, with scientists James Stewart and Ellie Hurer.

Electricity
Scientists James Stewart and Ellie Hurer guide you through the key facts about electricity for GCSE physics.

Energy
Learn all about energy for your GCSE physics exam, with Ellie Hurer and James Stewart.

Science exam techniques
Learn all about science exam techniques for your GCSE science exams with Dr Alex Lathbridge.

Energy
Changes in energy stores - AQA
Energy can be described as being in different ‘stores’. It cannot be created or destroyed but it can be transferred, dissipated or stored in different ways.

Work, power and efficiency - AQA
Energy is a key principle in physics, as it allows work to be done. The rate at which energy is transferred is called power and the amount of energy that is usefully transferred is called efficiency.

Energy and heating - AQA
Energy is transmitted by conduction, convection or radiation.The conductivity of materials can be compared by examining the time taken to transmit energy through them.

Energy demands - AQA
Every person, animal and device transfers energy. Much of that energy is supplied by electricity, which must be generated from other energy stores. Some of these are renewable but most are non-renewable.

Sample exam questions - energy - AQA
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps boost exam performance. Questions will include multiple choice, descriptions and explanations, using mathematical skills and extended writing.

Electricity
Electric circuits - AQA
Electrical current transfers energy around circuits. There are two types of current: direct and alternating.
Mains electricity - AQA
Electricity can flow either as direct or alternating current, and is used in homes to power electrical appliances. The National Grid distributes electricity throughout the country.

Static electricity - AQA
The motion of charged particles causes electrical effects, small shocks, lightning and sparks. Electrical fields cause forces to act on charged particles.

Sample exam questions - electricity - AQA
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps boost exam performance. Questions will include multiple choice, descriptions and explanations, using mathematical skills and extended writing.

Particle model of matter
Density of materials - AQA
Matter is made up of small particles called atoms. Atoms can exist on their own or together as molecules. Atoms are very small and around 100,000,000 of them end to end would measure 1 centimetre.

Temperature changes and energy - AQA
Changes in a material's temperature or state of matter are caused by changes to the internal energy. The energy required by different materials depends on their 'heat capacity' and 'latent heat'.

Particles in gases - AQA
Gases take up more space than solids or liquids and their particles are moving much faster. The temperature, pressure and volume of gases are all related.

Sample exam questions - states of matter - AQA
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps boost exam performance. Questions will include multiple choice, descriptions and explanations, using mathematical skills and extended writing.

Atomic structure
Models of the atom - AQA
The idea of the atom as the building block of matter has developed over time. What was thought of as a single particle about 1 × 10‾¹⁰ m across is now known to be a collection of smaller particles.
Atoms, isotopes and ions - AQA
Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons and electrons. Change the number of neutrons in an atom and it becomes an isotope, change the number of electrons, it becomes an ion.

Radioactive decay - AQA
With the wrong number of neutrons, nuclei can fall apart. A nucleus will regain stability by emitting alpha or beta particles and then ‘cool down’ by emitting gamma radiation.

Uses and dangers of radiation - AQA
People are exposed to sources of radiation in all aspects of everyday life. Radioactive sources can be very useful but need handling carefully to ensure safety.

Nuclear fission and fusion - AQA
The nuclei of atoms contain a large amount of energy. Releasing this energy would free the world from having to use fossil fuels. There are two methods of doing this: fission and fusion.

Sample exam questions - atomic structure - AQA
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Questions will include multiple choice, descriptions and explanations, using mathematical skills, and extended writing.

Forces
Scalar and vector quantities - AQA
Scientists often make measurements. The physical quantities they measure fall into two categories: scalars and vectors. Scalar and vector quantities are treated differently in calculations.
Contact and non-contact forces - AQA
Forces are responsible for all the interactions between particles and objects. They can be divided into two categories: contact forces and non-contact forces.
Gravity - AQA
Gravity is one of the most important forces in the universe. An object with mass in a gravitational field experiences a force known as weight.
Forces and elasticity - AQA
Forces are responsible for changing the motion of objects. If more than one force is present, the shape of an object can also be changed.

Moments, levers and gears - AQA
Turning forces are found in many everyday situations and are essential for machines to function. Levers and gears make use of these turning forces to provide an advantage.

Pressure in fluids - AQA
Every living thing on Earth is in balance with the pressure of the air or water around it. Pressure helps blood to move around the body and allows organisms to breathe.

Describing motion - AQA
The movement of objects can be described using motion graphs and numerical values. These are both used to help in the design of faster and more efficient vehicles.

Forces, acceleration and Newton's Laws - AQA
Falling objects eventually reach terminal velocity - where their resultant force is zero. Stopping distances depend on speed, mass, road surface and reaction time.

Momentum - Higher - AQA
Momentum can be thought of as a combination of mass and velocity. Momentum helps explain some of the most important interactions in nature.

Sample exam questions - forces - AQA
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps boost exam performance. Questions will include multiple choice, descriptions and explanations, using mathematical skills and extended writing.

Waves
Properties of waves - AQA
Waves are one way in which energy may be transferred between stores. Both mechanical and electromagnetic waves will transfer energy but not matter.

Transverse and longitudinal waves - AQA
Waves may be transverse or longitudinal. Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves with a wide range of properties and uses. Sound waves are longitudinal waves.

Reflection and refraction - AQA
All waves will reflect and refract in the right circumstances. The reflection and refraction of light explains how people see images, colour and even optical illusions.
Sound waves - AQA
Sound is caused by the vibration of particles but not all vibrations can be heard as sound. Common ideas about sound come from the limited range of vibrations that human ears can detect.

Lenses - AQA
Lenses are precisely shaped pieces of glass that have been developed and used in corrective glasses, telescopes, microscopes, binoculars, and magnifying glasses.

Black body radiation - AQA
All objects are continually absorbing and emitting infrared radiation. Black bodies are perfect absorbers and emitters of radiation.

Sample exam questions - waves - AQA
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps boost exam performance. Questions will include multiple choice, descriptions and explanations, using mathematical skills and extended writing.

Magnetism and electromagnetism
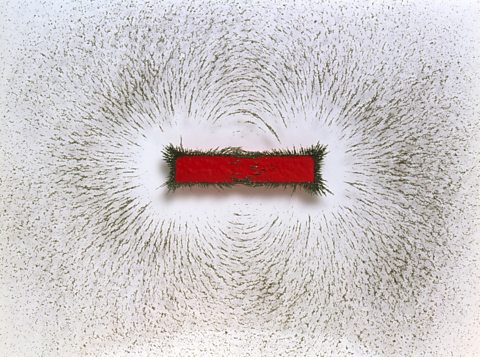
Magnetic fields - AQA
Magnetism is due to the magnetic fields around magnets. The fields can be investigated by looking at the effects of the forces they exert on other magnets and magnetic materials.
Electromagnets - AQA
Electromagnetism is due to the magnetic fields around electric currents. The fields can cause forces with other nearby magnets which can be used to make motors spin and loudspeakers produce sound.
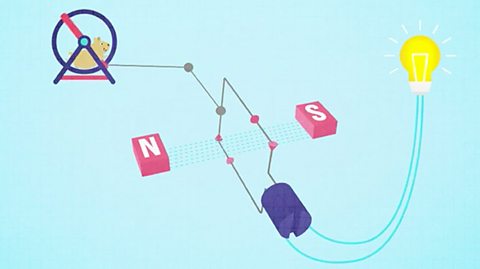
Electromagnetic induction - Higher - AQA
Electromagnetic induction can create a voltage by movement of a conductor in a magnetic field. This voltage can make current flow, and the effect is used in electricity generation and microphones.

Transformers - Higher - AQA
Transformers use electromagnetic induction to change the voltage of alternating currents. The voltage and current changes can be calculated, as the power transfer is constant.

Sample exam questions - magnetism and electromagnetism - AQA
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps boost exam performance. Questions will include multiple choice, descriptions and explanations, using mathematical skills and extended writing.

Space physics
The Solar System - AQA
The Sun is our nearest star. It is a relatively small star when compared to other stars in the universe. Our Solar System contains the Sun and everything that orbits it.
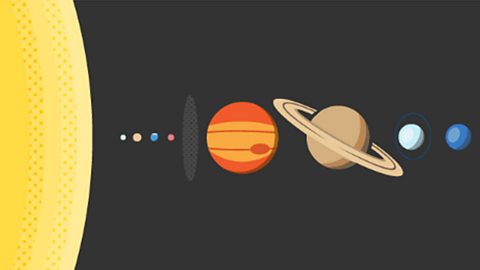
The life cycle of a star - AQA
Gravity and nuclear fusion reactions drive the formation and development of stars. Stars with different masses grow and change throughout the different stages of their lives.

The expanding Universe - AQA
Theories about the development of the Universe, such as the Big Bang theory, are based on astronomical observations and ideas such as red-shift and dark energy.

Sample exam questions - space physics - AQA
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Questions will include multiple choice, descriptions and explanations, using mathematical skills, and extended writing.

Practical skills
Scientific skills - AQA
Scientific investigations have several stages - planning, collecting data, analysing data and evaluation. It is important to understand how to carry out each stage of the investigation.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link