Antarctic ice crack takes major turn
- Published
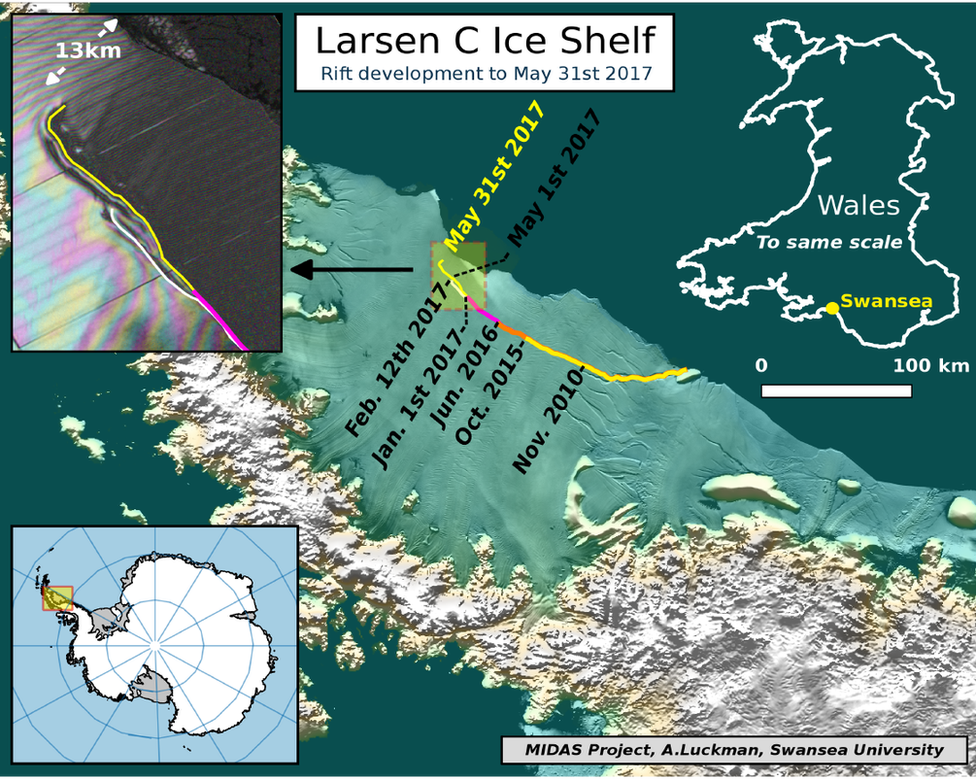
There has been an important development in the big crack cutting across the Larsen C Ice Shelf in Antarctica.
The fissure, which threatens to spawn one of the biggest bergs ever seen, has dramatically changed direction.
"The rift has propagated a further 16km, with a significant apparent right turn towards the end, moving the tip 13km from the ice edge," said Swansea University's Prof Adrian Luckman.
The calving of the berg could now be very close, he told ģÉČËŋėĘÖ News.
However, he also quickly added that nothing was certain.
The fissure currently extends for about 200km in length, tracing the outline of a putative berg that covers some 5,000 sq km - an area about a quarter of the size of Wales.
The crack put on its latest spurt between 25 May and 31 May. These dates were the two most recent passes of the European Union's Sentinel-1 satellites. Their radar vision is keeping up a constant watch as the White Continent moves into the darkness of deep winter.
After some initial activity at the beginning of the year, the Larsen crack became stationary as it entered what is termed a "suture" zone - a region of soft, flexible ice. But this situation held only until the beginning of May, when the rift tip then suddenly forked. And it is the new branch that has now extended and turned towards the ocean.
When the berg's calving does finally take place, the block will probably drift away quite gradually from the ice shelf.
"It's unlikely to be fast because the Weddell Sea is full of sea-ice, but it'll certainly be faster than the last few months of gradual parting. It will depend on the currents and winds," explained Prof Luckman.
Taking out such a large chunk of ice would mean the Larsen C shelf would lose more than 10% of its area. Previous research by the Swansea group has shown that this will put the shelf in a much less stable configuration.
Similar calving events on the more northerly Larsen A and Larsen B ice shelves eventually led to their total break-up. Scientists are concerned that this same fate could now await Larsen C.
Were the shelf to collapse (and even if it did, it would still take many years to complete), it would continue a trend across the Antarctic Peninsula.
In recent decades, a dozen major ice shelves have disintegrated, significantly retreated or lost substantial volume - including Prince Gustav Channel, Larsen Inlet, Larsen A, Larsen B, Wordie, Muller, Jones Channel, and Wilkins.
Prof Luckman's MIDAS Project is posting updates on the Larsen crack , and on .
Jonathan.Amos-INTERNET@bbc.co.uk, external and follow me on Twitter:
- Published2 May 2017
- Published30 April 2017