What do you know?
What type of graph is presented as a circle divided into segments?
A pie chart is presented as a circle divided into segments.
Key points
- There are a variety of different types of graphs that can be used to show geographical data.
- graphA diagram showing the relationship between two variable quantities each measured along a pair of axes. can be used to show patterns.
- Graphs can be used to help reach conclusions.
Types of graph
In geography it is important to be able to read and understand data that is presented in a range of different ways. We often use graphs to present data in a clear and accessible way. There are many different types of graphs but those used most frequently in geography are described below.
Video: Using graphs in geography
Using graphs in geography
Using graphs in geography.
Graphs can help you organise and display data you've collected, like facts and figures about sustainable transport. Different types of graph have different uses.
A line graph shows how data changes over time. For example, how the volume of traffic changes over a day so you can see the busiest times.
A bar chart is best for comparing groups of data. For example, which modes of sustainable transport are most commonly used in a day. Here each bar represents a different mode: bus, tram, electric car and bicycle.
And use a scatter graph to see if there is a link between two sets of data. For example, between the number of charging points and the number of electric cars in different cities in the UK.
Graphs help us understand data and reach conclusions.
Line graphs
Line graphs are used to show continuous changes over time. A line graph might be useful for showing the pattern of change in world population, for example.
The line graph below shows the population growth of low income, middle income, and high income countries between 1960 and 2020.
Population growth from 1960 to 2020
Scatter graphs
Scatter graphs show how two sets of data are related to each other. Data points are plotted on a graph and then a line of best fit is drawn to show the overall trendThe overall direction of the data. For example, upward or downward. if there is one. The trend is usually described as a correlationThe relationship between two sets of data. Usually described as positive or negative.. When the line of best fit has a positive gradientAnother word for steepness. On a graph, the gradient is defined as being the change in the 'y' value divided by the change in the 'x' value. The steeper the line, the larger the gradient. , there is positive correlation. If the line of best fit has a negative gradient, there is a negative correlation.
Scatter graphs
Bar charts
Bar charts are used to compare different categories. The bars must be separated by gaps because the categories are unconnected.
The bar chart below shows different types of vehicle that were seen during a traffic survey.
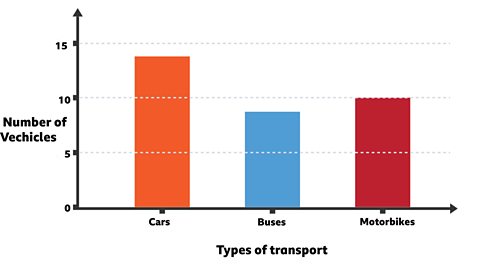
Histograms
Histograms look similar to bar charts as they both display data using bars. A histogram shows continuous data, such as different age groups, and therefore the bars are drawn without gaps between them.
The population pyramidA graph showing the number or percentage of people in different age groups divided by gender. below shows the age range of people in Japan's population.
Population pyramid of Japan
Pie charts
Pie charts are represented as a circle divided into segments. A full pie chart represents 100% and each slice, or segment, shows what proportionA part, share, or number considered in comparison to the whole, eg 1 in 10. that category is of the whole.
The pie chart below shows the estimated population of Europe in 2021. Each segment of the chart represents a different age range, showing what percentage of the population is in each age group.
Population pie chart
Combined graphs
Sometimes, graphs may be combined together. For example, a climate graph and a flood hydrograph both present data using a bar chart and a line graph in a single graph.
Storm hydrograph
Although these graphs can appear complicated, focus on the three boxes at the top - peak rainfall, lag time and peak discharge. The graph is showing how long it takes rainfall water to reach the rivers.
Question
What would be the most appropriate type of graph to show the changes in calorie consumption over time?
A line graph would be best as it shows continuous change over a period of time.
Quiz: Types of graph
Understanding graphs
Describing a graph
When examining data on a graph, there are certain things to look for, such as the overall trend, the rate of change, and any anomalyData which is significantly different than what is expected and that doesn't fit the overall pattern.. When describing what a graph shows, it is best to deal with each of these in turn.
Step 1 - describe the overall trend.
Eg: The population is increasing.
Step 2 - describe the rate of change.
Eg: The increase has been rapid.
Step 3 - point out any data points that don't fit the overall pattern. These are called anomalies.
Eg: The increase was rapid, apart from in 2008 when it slowed.
Step 4 - include some figures as evidence.
Eg: The increase was rapid, changing from 1 billion in 1800 to 7 billion in 2011.
Interpreting a graph
Interpreting a graph means to explain why it shows what it does. It may be that the population of a country has increased because of improvements in health care, for example. You should consider why anomalies exist. For example, a war may cause a fall in population.
Anomaly on a graph
Question
What is an anomaly?
An anomaly is a data point which does not fit the overall trend or pattern. On a line graph this might look like a sudden decrease, increase or significant change in the data.
Quiz: Understanding graphs
Play the Planet Planners game! gamePlay the Planet Planners game!
Make decisions for the planet in this KS3 geography game.

More on Geographical skills
Find out more by working through a topic
- count5 of 10

- count8 of 10
