Computational thinking
Introduction to computational thinking
Before computers can be used to solve a problem, the problem itself and the ways in which it could be resolved must be understood. Computational thinking techniques help with these tasks.

Decomposition
Before computers can solve a problem, the problem and the ways in which it can be resolved must be understood. Decomposition helps by breaking down complex problems into more manageable parts.
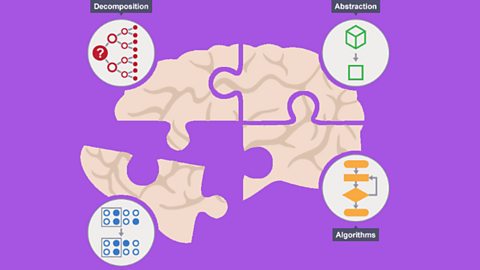
Pattern recognition
Once we have decomposed a complex problem, it helps to examine the small problems for similarities or ‘patterns’. These patterns can help us to solve complex problems more efficiently.

Abstraction
Once we have recognised patterns in our problems, we use abstraction to gather the general characteristics and to filter out of the details we do not need in order to solve our problem.

Algorithms
An algorithm is a plan, a set of step-by-step instructions to resolve a problem. In an algorithm, each instruction is identified and the order in which they should be carried out is planned.

Evaluating solutions
Before solutions can be programmed, it is important to make sure that it properly satisfies the problem, and that it does so efficiently. This is done through evaluation.
Algorithms
Designing an algorithm
Before designing an algorithm it is important to first understand what the problem is. Algorithms can be designed using pseudocode or a flowchart, and the standard notations of each should be known.

Searching
Searching for data can be very difficult. Searching algorithms, such as linear search and binary search, make the process of searching for data much easier.

Sorting
Putting data into order can be difficult and time consuming. Sorting algorithms, such as bubble sort and bucket sort can help with this.

Sequencing
When designing algorithms, it is important to make sure that all the steps are presented in the correct order. This is known as sequencing, and can be displayed in pseudocode or flowcharts.

Selection
When designing algorithms, there are many steps where decisions must be made. This decision is known as selection, and can be displayed in pseudocode or flowcharts.

Iteration
When designing algorithms, there may be some steps that need repeating. This is known as iteration, and can be displayed in pseudocode or flowcharts.
Logical reasoning
There is almost always more than one solution to a problem. Logical reasoning is used to predict the outcomes of the algorithms that are designed to solve a problem, to help select the best solution.

Programming
Introduction to programming
Programming is writing computer code to create a program, in order to solve a problem. Programs consist of a series of instructions to tell a computer exactly what to do and how to do it.
Programming basics
Programming is writing computer code to create a program, in order to solve a problem. To program a computer, you need to know how programs are constructed.

Selection in programming
When designing programs, there are often points where a decision must be made. This decision is known as selection, and is implemented in programming using IF statements.

Iteration in programming
When designing programs, there may be some instructions that need repeating. This is known as iteration, and is implemented in programming using FOR and WHILE statements.

Boolean logic
When designing programs, there are often points where a condition needs to be tested in order to make a decision. Conditions are formed using Boolean logic.

Arrays and lists
When writing programs, it is useful to use arrays and lists as they simplify programs by storing related data under one name.

Procedures and functions
When writing programs, we should avoid long, repetitive code. Procedures and functions help to keep our programs simple and short.

Writing error-free code
When writing programs, code should be as legible and error free as possible. Debugging helps keep code free of errors and documenting helps keep code clear enough to read.

Data representation
Binary
Computers use binary to process data. There are simple techniques to convert between binary and denary and to add two binary numbers together.
Representing text, images and sound
Learn how text, images and sound are converted into binary so they can be processed by a computer and how images and sound are compressed to create smaller files.

Hardware and software
Digital devices
Computers exist in many digital devices that we use on a day-to-day basis. Digital devices may be input, output or storage devices. On a basic level, they all operate through the use of logic gates.

Software
Software is the programs that are run on computer hardware. There are two different types of software: systems software and applications software.

The CPU and the fetch-execute cycle
Learn about what the central processing unit is, its three main components, the factors that influence the CPU’s speed, and the fetch-execute cycle.

Introduction to networks
The two main types of network are wide area networks and local area networks. Learn what these are, and the benefits and problems of using them.

Internet communication
Internet and communication
As a society we need to communicate and share. The internet allows us to communicate and share information in a matter of seconds.

Search engines
The internet contains billions of pages of information. You use search engines to help you filter through the pages to find the information you need.

Safety and responsibility
Online safety
The internet is a fantastic tool and resource. By taking simple precautions, online dangers can largely be avoided and we can stay safe while online.

Bias and reliability
We use the internet to find information. However, finding information that is reliable and free of bias is as important as finding the information itself.

The law and ethics
Computer-related laws exist to protect users. By being aware of the laws we can stay safe whilst online.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription