Evidence
Four types of evidence
When you look back at history nothing is a simple as it might seem. Always remember to ask why and look for clues in written, visual, oral and physical evidence.

Using evidence
Interpreting evidence is vital in the study of history. If you check the sources of your information thoroughly, you will get as close to the truth as you can.

Using evidence in your arguments
Sometimes we don’t even pay attention to the evidence about our own lives. Are you sure that’s the way things happened, or are you changing the facts to suit your own interests?

The Normans
Claimants to the throne in 1066
The death of Edward the Confessor in 1066 set off a year of turmoil in England. Three different people believed that they were entitled to the English throne.

The Battle of Hastings
The Battle of Hastings took place on 14 October 1066. William of Normandy was crowned King of England on Christmas Day.

What was life like in medieval society?
Most medieval people lived in villages, as there were few large towns in the Middle Ages. The majority of people were peasants.

The feudal system
The feudal system helps us to understand how medieval society was organised. There was a big divide between wealthy nobles and peasants.

Why did the Nomans come to Ireland?
Find out what brought the Normans to Ireland in the 12th Century.

Life in Ireland after the Normans
Explore the influence and impact the Normans had in Ireland.

Rights and the Rule of Law
The United Irishmen
Discover more about the United Irishmen their rebellions and how they fought for democratic change in Ireland.

Ireland and the French Revolution
Find out why Ireland and the United Irishmen were so influenced by the French Revolution.

Catholics and the Act of Union
Find out how Ireland's Catholic population reacted to the Act of Union in 1801.

The Act of Union and Unionism
Discover how the Act of Union led to a rise in unionism in Ireland and opposition to ≥…»ÀøÏ ÷ Rule.

≥…»ÀøÏ ÷ Rule and Nationalists
Find out how ≥…»ÀøÏ ÷ Rule and Nationalists' desire for self governance changed Ireland.

Opposition to ≥…»ÀøÏ ÷ Rule
Discover the factors that contributed to Unionist objections to ≥…»ÀøÏ ÷ Rule and their campaign and strategy against it.

Medicine through time
Causes and effects of the Black Death
In 1348, the Black Death reached Britain. Medieval medicine was incapable of finding a cure, and it is estimated that over 2 million people lost their lives during the outbreak.

The Great Plague
In 1665, the plague arrived in England once again. In London alone, at least 68,596 people died from the disease, and thousands across the country were killed.

Tudors and Stuarts
Who was Henry VIII?
Henry VIII is remembered for his six wives and his military success. His decision to break from the Catholic Church kickstarted the English Reformation.

Who was Elizabeth I?
Elizabeth I ruled England for 45 years. The country saw lots of change during her reign, with religion, trade and international exploration all very different by the time she died.

Elizabethan rule
Elizabeth I's reign has often been described as a ‘Golden Age’ of culture, wealth and exploration. Some historians, however, have begun to question just how accurate this is.

Slavery
Belfast and abolition
Many clear-thinking and humane citizens of Belfast campaigned against the slave trade, putting pressure on businesses and people that were part of it.

The slave traders
The trade in enslaved people was one of the most terrible aspects of our history. Some wealthy businessmen in Belfast engaged in it without any criticism from society.

The slave trade and Belfast
Even though the people of Belfast tend to view slavery as something that happened on the other side of the world, many of the city’s businesses were closely linked to it.

What was precolonial West Africa like?
A number of powerful kingdoms developed in precolonial West Africa. They each had their own diverse cultures, art, histories and religions.

The transatlantic slave trade
The transatlantic slave trade was the largest forced migration in history. Over two million Africans died during the journey to the Americas, a journey known as the middle passage.

The experiences of enslaved people
Life as an enslaved person on the plantations was brutal. People still found ways to empower themselves through religion, language, culture, music and revolution.

The abolition of the slave trade
The Abolition of the Slave Trade Act was a movement developed in Britain to end the slave trade. However, hundreds of thousands of people remained enslaved.

Reformation
The Reformation and its impact
In 1534, Henry VIII declared that he was the head of the Church in England, not the Pope. This was the beginning of the English Reformation.

Religious conflict in Ireland
The United Irishmen
Discover more about the United Irishmen their rebellions and how they fought for democratic change in Ireland.

Ireland and the French Revolution
Find out why Ireland and the United Irishmen were so influenced by the French Revolution.

Catholics and the Act of Union
Find out how Ireland's Catholic population reacted to the Act of Union in 1801.

The Act of Union and Unionism
Discover how the Act of Union led to a rise in unionism in Ireland and opposition to ≥…»ÀøÏ ÷ Rule.

≥…»ÀøÏ ÷ Rule and Nationalists
Find out how ≥…»ÀøÏ ÷ Rule and Nationalists' desire for self governance changed Ireland.

Opposition to ≥…»ÀøÏ ÷ Rule
Discover the factors that contributed to Unionist objections to ≥…»ÀøÏ ÷ Rule and their campaign and strategy against it.

The Industrial Revolution
The growth of industrial Belfast
Find out how the Industrial Revolution impacted Belfast and changed it forever.

Belfast and shipbuilding
Find out how Belfast became on of the most important shipbuilding cities in the world - and built the world's most famous ship.

Life in Industrial Belfast
Find out what life was really like in Belfast during the Industrial Revolution.

The origins of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution in Britain brought huge technological advances, which had a big impact on people’s lives. However, not all of these changes were positive.

History makers
Clara 'Ma' Copley
Clara 'Ma' Copley was a boxing promoter in Belfast in the early 20th Century.

Lilian Bland
Lilian Bland was the first woman in the world to design and build her own aeroplane.

Anne Crawford Acheson
Anne Crawford Acheson used her artistic talent to help wounded soldiers in the First World War.

Annie Maunder
Annie Maunder was an astronomer who captured the longest coronial streamer (a ray like structure coming out from the sun) on record.

William McCrum
William McCrum invented the penalty kick.

Oliver Pollock
Oliver Pollock is credited with inventing the US dollar sign.
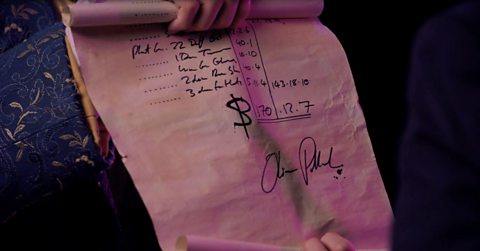
Mary Ann McCracken
Mary Ann McCracken was a social reformer in the 18th Century

Samuel McGaughey
Sir Samuel McGaughey was a sheep farmer and philanthropist who had the nickname 'the sheep king'.

Mary Mallon
Mary Mallon was also known as'Typhoid Mary' as she unknowingly carried typhoid and infected many people.

Barney Hughes
Barney Hughes was a successful baker and philanthropist who invented the'Belfast bap'

Kennedy Kane 'Ken' McArthur
Kennedy Kane McArthur won Gold in the marathon at the 1912 Stockholm Olympics

James Martin
James Martin invented the ejector seat.

John Clarke
John Clarke was known as 'the potato wizard'.

Dr Elizabeth Bell
Dr Elizabeth Bell was one of the first female doctors in Ireland, a feminist and advocate for women’s rights.

John McAlery
John McAlery introduced association football to Ireland.

Northern Ireland in the early 20th Century
Belfast and shipbuilding
Find out how Belfast became on of the most important shipbuilding cities in the world - and built the world's most famous ship.

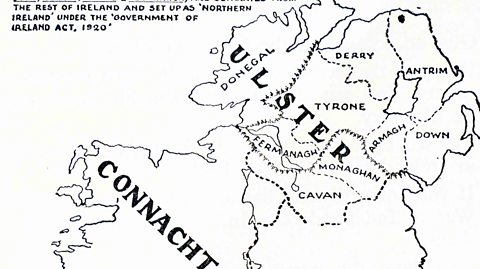
The events that led to the partition of Ireland
Find out more about the events that led to the partition of Ireland into Northern Ireland and the Irish Free State.
Suffragettes
Suffragettes in prison
Society treated the suffragettes like criminals and put them in jail. However, many went on hunger strike in protest. Eventually the government had to change their attitude.

The Suffragette Movement
Only just over a hundred years ago, men and women were not considered to be equal. This angered some women so much that they took matters into their own hands.

Why become a suffragette?
By becoming a suffragette, women could show society that they weren’t prepared to put up with inequality. Doing nothing wasn’t an option!

World War One
Causes of World War One
When World War One started millions of men volunteered to fight. Were they fearless patriots doing their duty or unlucky victims of government propaganda?

Propaganda and conscription
Many young men who joined up to fight in WW1 thought that it would be a brief and glorious adventure – they felt they were doing the right thing for their family and friends.

Trench warfare
The reward of answering the call for army recruits was the horror of trench warfare with its rats, disease, mud, constant shelling and shooting and fear of imminent death.

What was life like on the front line in World War One?
Life in the trenches of World War One was very difficult. The first day of the Battle of the Somme, in 1916, was the deadliest day in the history of the British army.

The end of World War One and the Treaty of Versailles
World War One ended on 11 November 1918, with the surrender of Germany. The Treaty of Versailles punished Germany for their involvement in starting the war.

Germany
What challenges did Germany face after World War One?
The Treaty of Versailles severely punished Germany for its involvement in World War One. From 1918 to 1933, the German people lived through much economic hardship.

World War Two: An overview
Britain declared war on Germany on 3 September 1939. The war lasted until 1945 when Japan surrendered.

Causes and consequences of partition
≥…»ÀøÏ ÷ Rule and Nationalists
Find out how ≥…»ÀøÏ ÷ Rule and Nationalists' desire for self governance changed Ireland.

Opposition to ≥…»ÀøÏ ÷ Rule
Discover the factors that contributed to Unionist objections to ≥…»ÀøÏ ÷ Rule and their campaign and strategy against it.

The events that led to the partition of Ireland
Find out more about the events that led to the partition of Ireland into Northern Ireland and the Irish Free State.
