Applied anatomy and physiology
Muscular system - WJEC
This system is mainly concerned with producing movement through muscle contraction. This section explores the different types of muscles in our body and their involvement in sporting activities.

Skeletal system - WJEC
The skeleton is the central structure of the body and is made up of bones, joints and cartilage. The skeleton provides the framework for muscles and gives the body its defined human shape.
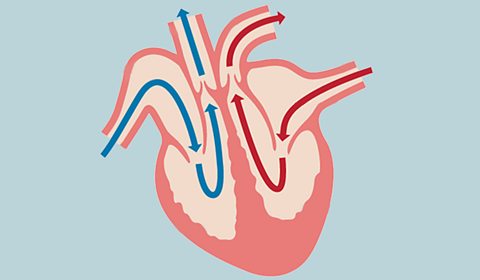
Cardiovascular system - WJEC
The cardiovascular system is made up of three main parts - the heart, the blood vessels and the blood that flows through them.
Cardio-respiratory system - WJEC
The respiratory system transports oxygen from the air we breathe, through a system of tubes, into our lungs and then diffuses it into the bloodstream, whilst carbon dioxide makes the opposite journey.
Aerobic and anaerobic exercise¬Ý- WJEC
Depending upon whether the body uses oxygen or not in order to perform physical activities determines if the activity is aerobic (with oxygen) or anaerobic (without oxygen).

Long and short term effects of exercise - WJEC
During exercise the body systems respond immediately to provide energy for the muscles to work. After regular and repeated exercise, these systems adapt to become more efficient.

Movement analysis - WJEC
To help people understand the different types of movement in sport, specific terminology is used so that it is clear exactly what types of movements have taken place in order to analyse that movement.

Physical training
Health, fitness and exercise - WJEC
Health, fitness and exercise are essential to the sporting and life performance of humans. The relationship between the three is cyclical.

Principles of training - WJEC
Training means exercising regularly to improve skills and fitness. The training that an athlete does must be appropriate for that person and their sport in order to get the most out of their training.

Methods and effects of training - WJEC
There are a number of different ways of training that can improve health and fitness necessary for a range of activities. Warming up and cooling down are essential parts of a training session.

Sport psychology
Classification of skill - WJEC
Sport and physical activities require different sets of skills. Skills have many characteristics and can change depending on the environment, complexity and pace of the skill which is carried out.

Guidance - WJEC
Performers need guidance to acquire and improve their skills. Visual, verbal, manual and mechanical guidance are used in different situations and to support performers in a range of different ways.

Feedback - WJEC
Feedback tells performers how well they performed. It is a vital component of the information processing model and can focus on knowledge of results or performance and can be intrinsic or extrinsic.
Mental preparation - WJEC
To succeed and perform their best, athletes need to use their minds as well as their bodies. Mental techniques help to control emotions, manage stress and improve participation and performance.

Goal setting - WJEC
Setting targets helps participants develop strategies for success. This has an impact on health, wellbeing and performance and helps focus attention and enable improved effort and concentration.

Socio-cultural influences
Social groupings - WJEC
Participation in sport is influenced by social factors, such as people’s age, gender, disability, ethnicity, friendship group and family.

Ethical factors - WJEC
Sport requires people to follow written and unwritten rules to make it fair. It expects people to behave responsibly to ensure respect, fairness and safety. In this way, it promotes social values.

Commercialisation - WJEC
Sport is not just about participation. It is also part of the commercial world, managed and marketed to make money. Sponsorship and the media are now significant influences on sport.

Technology in sport - WJEC
Technology affects many aspects of sport from performance on and off the field to spectating and public profile. Increasingly, advances in technology influence grass-roots as well as elite sport.

Health, fitness and well-being
Health and wellbeing - WJEC
Physical activity is an essential part of a healthy lifestyle. Linked to other positive lifestyle choices, it promotes good physical health and contributes to people’s emotional and social wellbeing.

Sedentary lifestyles - WJEC
Many people in our society lead inactive lifestyles due to passive job roles, leisure activities and, sometimes, a lack of opportunity. Sedentary lifestyles can cause poor health.

Diet and nutrition - WJEC
People need to manage the quantity, type and proportion of foods that they eat as part of a healthy lifestyle or, for sportspeople, as part of a training and performance regime.

Exam skills
Exam techniques - WJEC
An exam is designed to find out how much you understand about a subject. There are some key techniques that you can learn to help you do as well as possible for each type of exam question.

Sample exam questions - WJEC
You will be taking a theory exam for part of your GCSE PE course and the paper will contain a range of questions across all the subject content that you have studied.

Performance analysis
Rules, regulations and terminology - WJEC
To participate safely, fairly and effectively, sportspeople must understand the terms used in their sports and adhere to the rules and regulations. They must also manage any risks.

Observing and analysing performance - WJEC
To help athletes to improve, coaches and performers need to observe and analyse athletes’ movements during performance. They use this data to monitor progress and provide effective feedback.
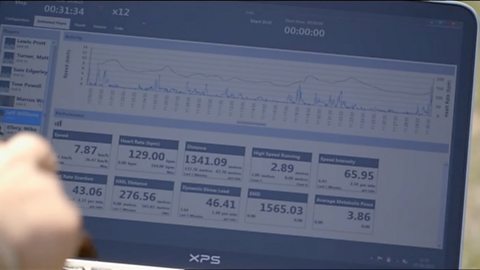
Evaluating performance - WJEC
Having identified the athlete’s strengths and areas for improvement, coaches and performers use the data to develop training programmes that improve the athlete’s skills and fitness.

Planning strategies, tactics and practices - WJEC
Coaches and performers use performance analysis technology to develop and improve the strategies and tactics that athletes use during team and individual performances.

Writing a Personal Fitness Programme (PFP) - WJEC
Athletes must design a personal training programme with the aim of improving performance in one of their practical activities. . This is designed to suit their individual needs.

Practical performance
- Guide Number2 Guides

- Guide Number2 Guides

- Guide Number2 Guides

- Guide Number2 Guides

- Guide Number2 Guides

- Guide Number2 Guides

- Guide Number2 Guides

- Guide Number2 Guides

- Guide Number2 Guides

- Guide Number2 Guides

- Guide Number2 Guides

- Guide Number2 Guides

- Guide Number2 Guides

- Guide Number2 Guides

- Guide Number2 Guides

- Guide Number2 Guides

- Guide Number2 Guides

- Guide Number2 Guides

- Guide Number2 Guides

- Guide Number2 Guides

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link